Are you tired of Chrome’s minimalist URL display? Let’s bring back the familiar HTTPS and WWW. This guide will walk you through the simple steps to restore the full URL format in your Chrome browser.
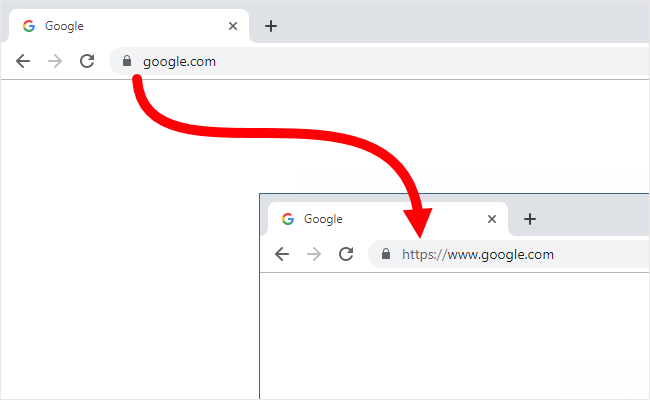
Why Restore HTTPS and WWW?
While Chrome’s simplified approach has its appeal, many users prefer the clarity and security benefits of seeing the complete URL. Here’s why:
1. Security Verification: Quickly confirm if a website uses a secure HTTPS connection.
2. Domain Identification: Easily recognize the website’s domain without ambiguity.
3. Troubleshooting: Provide more detailed information when debugging website issues.
Restore HTTPS and WWW in Website URLs in Chrome
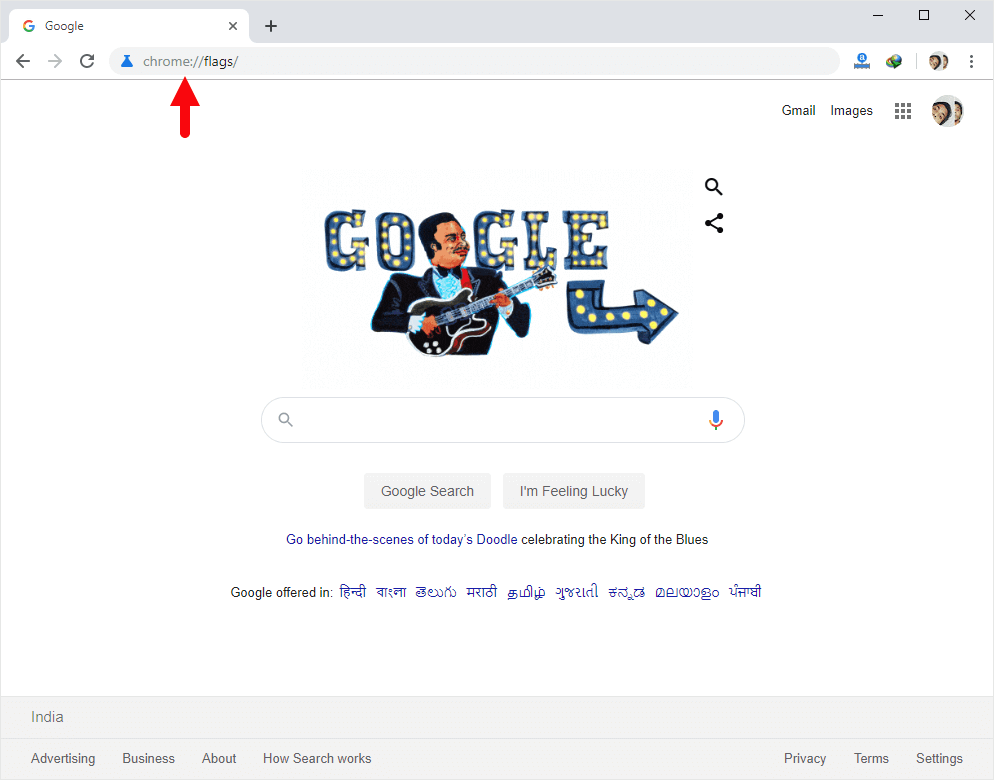
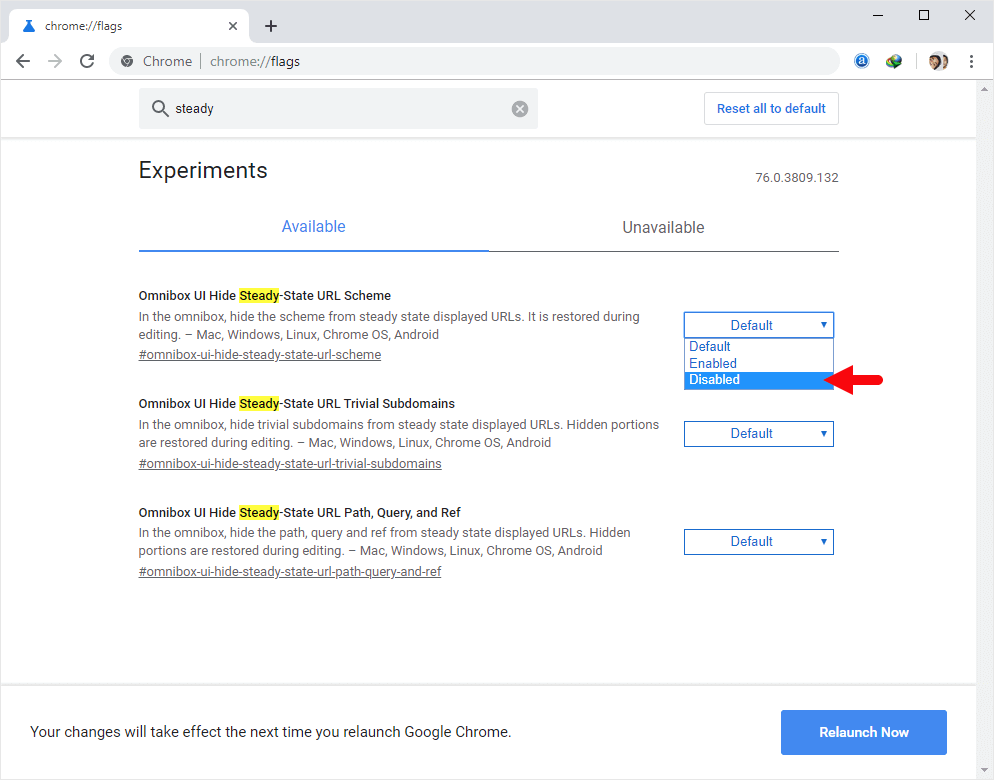
- In the address bar type chrome://flags/ and press Enter.
- Use the search bar at the top of the Chrome Flags page to find “Steady.”
- You should see three flags related to URL display:
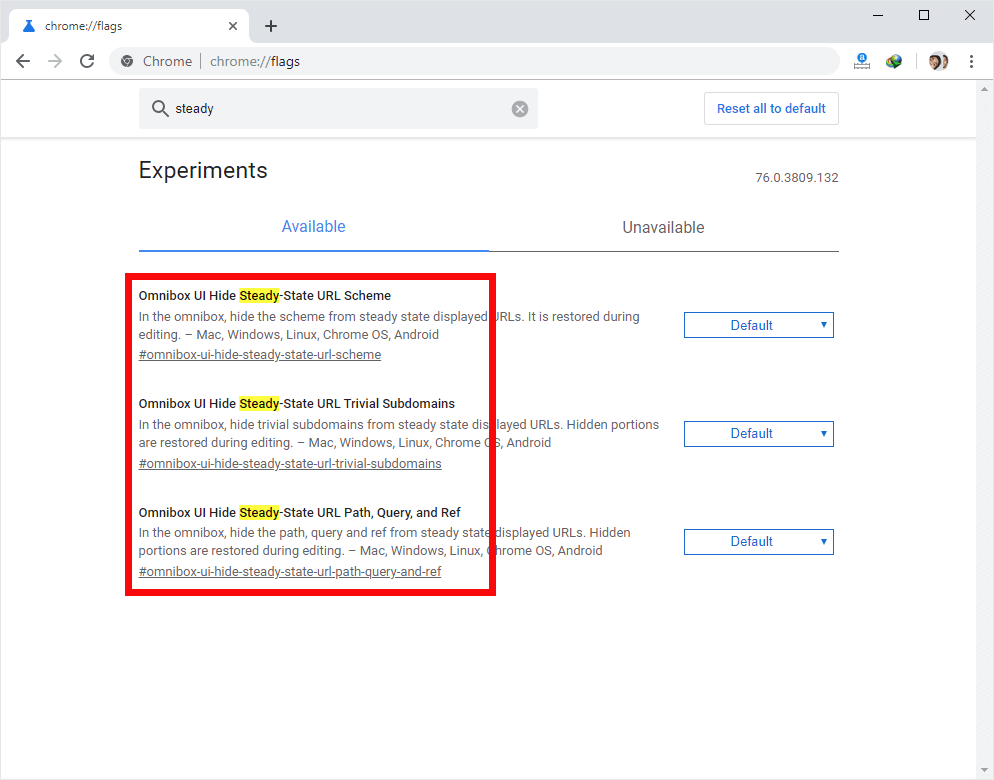
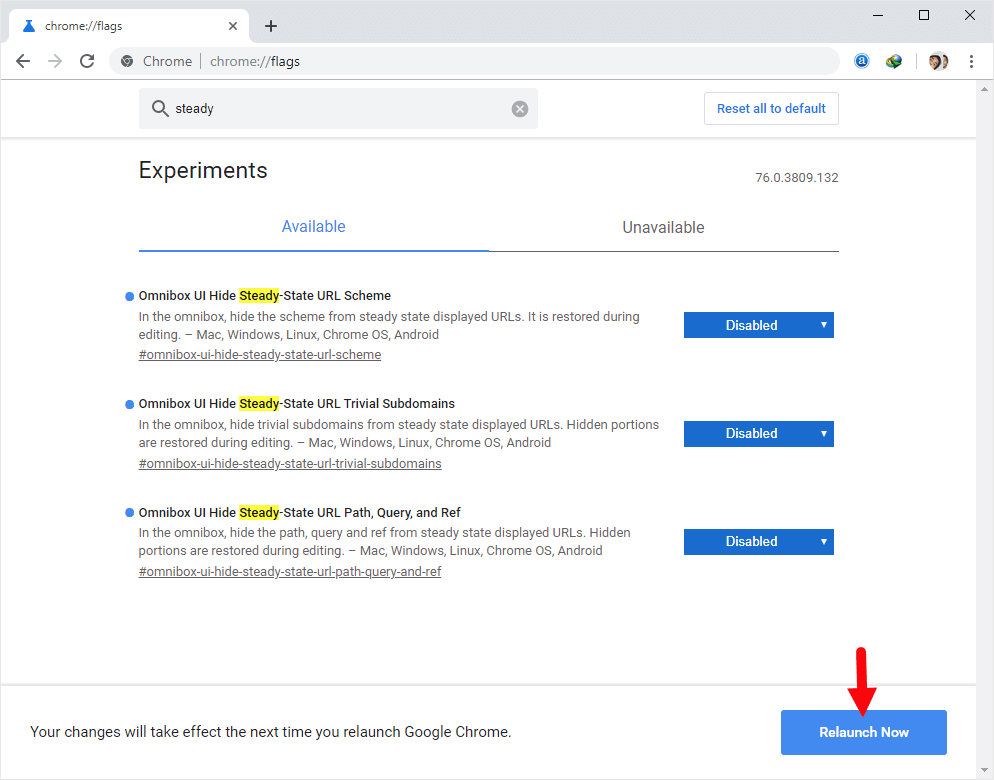
- Disable the Flags (for each Steady flag, click the default dropdown menu and select “Disabled”).
- At the bottom of the Chrome Flags page, click the “Relaunch” button.
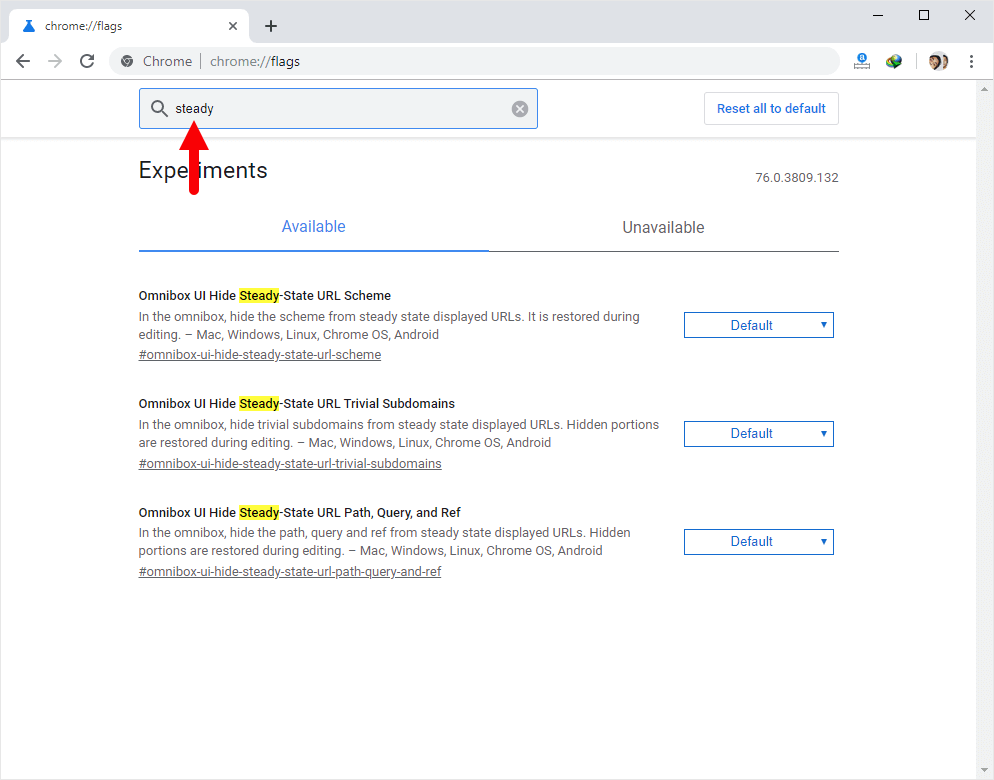
– Omnibox UI Hide Steady-State URL Scheme
– Omnibox UI Hide Steady-State URL Trivial Subdomains
– Omnibox UI Hide Steady-State URL Path, Query, and Ref
That’s it. Once Chrome restarts, you should see the full HTTPS and WWW displayed in the address bar for compatible websites.
Additional Resources
- Re-enabling HTTPS and WWW? If you’ve previously hidden these elements and want to restore them, follow the same steps but select “Default” instead of “Disabled” for the Steady flags.
- HTTPS Limitations While this guide restores the visual display of HTTPS and WWW, it doesn’t guarantee a secure connection. Websites must implement HTTPS correctly for it to be secure.
- Chrome Guides: If you are searching for How-to Guides for Google Chrome, please visit the Google Chrome Guides page.